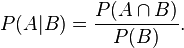
| Multiplication Rule: When two events, A and B, are dependent, the probability of both occurring is: P(A and B)= P(A)xP(B|A) |
Example- A math teacher gave her class two tests. 25% of the class passed both tests and 42% of the class passed the first test. What percent of those who passed the first test also passed the second test?
| Start with Multiplication Rule 2. | ||
| Divide both sides of equation by P(A). | ||
| Cancel P(A)s on right-hand side of equation. | ||
| Commute the equation. | ||
| We have derived the formula for conditional probability. | ||
No comments:
Post a Comment